Manifold Path Guiding for Importance Sampling Specular Chains
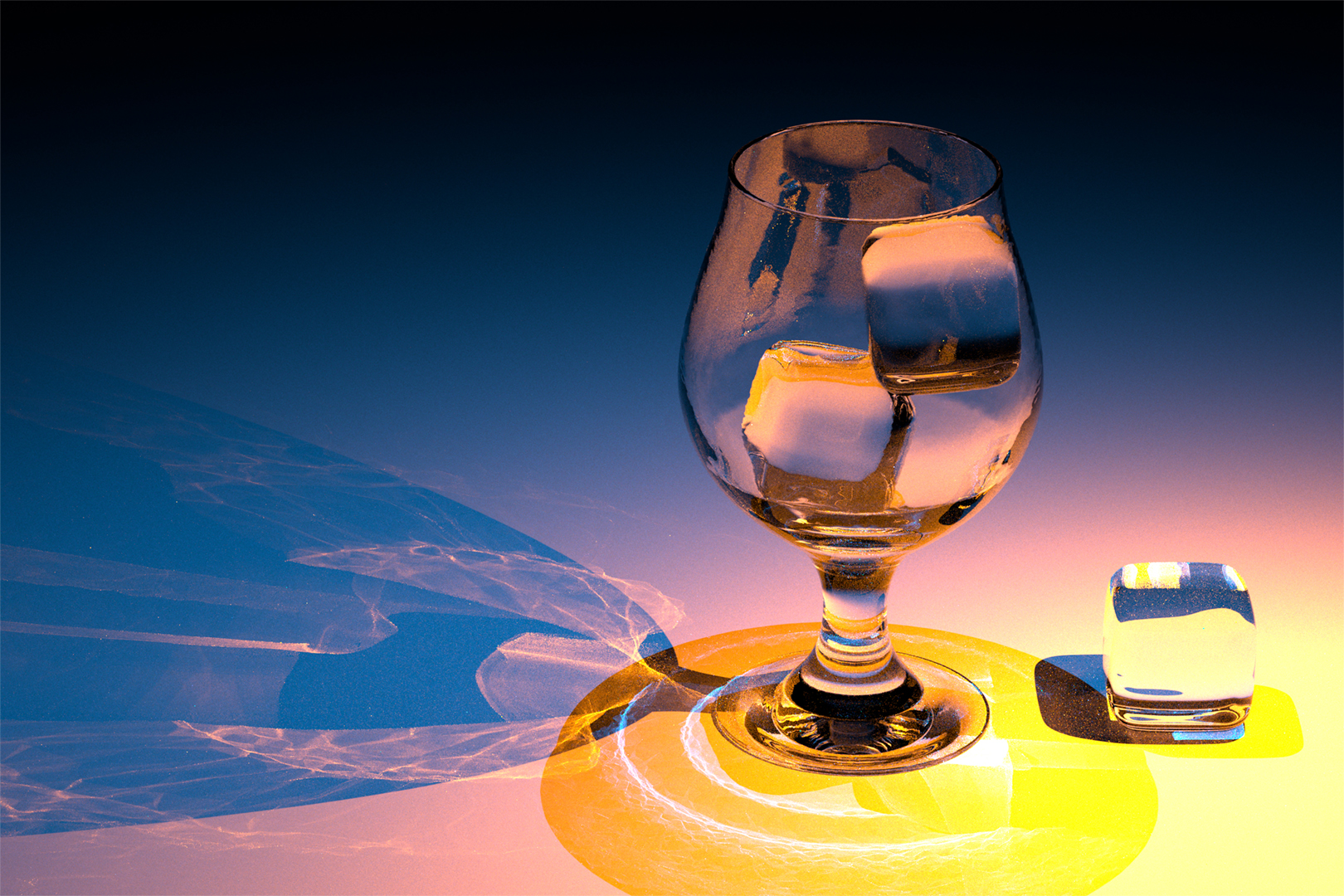
Complex visual effects such as caustics are often produced by light paths containing multiple consecutive specular vertices (dubbed specular chains), which pose a challenge to unbiased estimation in Monte Carlo rendering. In this work:
- We analyze light transport behavior within sub-paths containing specular chains and non-specular separators.
- We leverage specular manifolds to reconstruct continuous energy distributions from historical/coherent sub-paths.
- We propose manifold path guiding, a progressive pipeline to importance sample paths with long specular chains via seed chain generation and manifold walks.
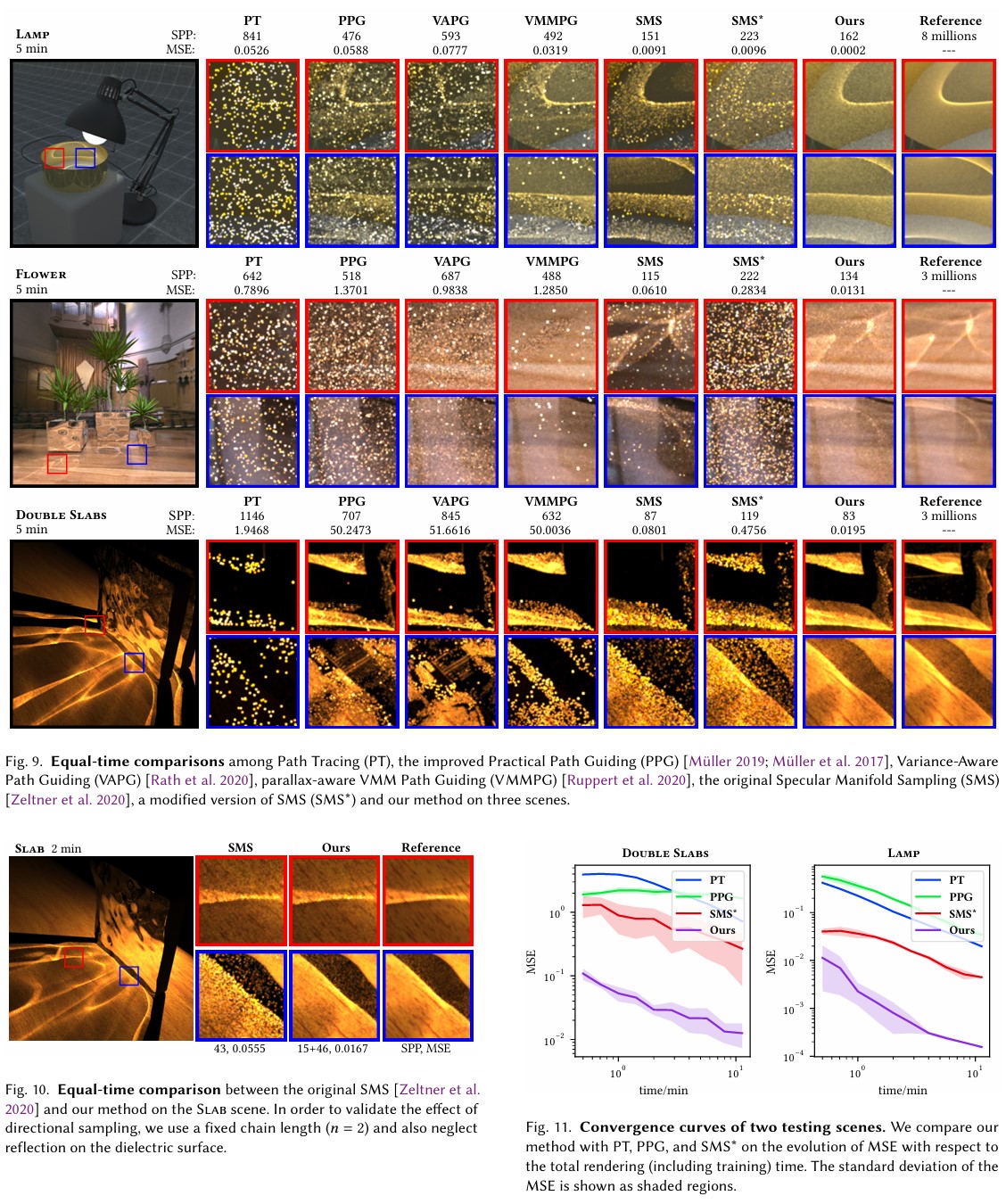
Our method achieves up to 40× variance reduction compared to state-of-the-art unbiased methods, particularly in scenes with long specular chains and complex visibility.
Limitations of Existing Approaches
| Method | Shortcomings |
|---|---|
| MLT-based | Struggles with SDS paths despite specialized mutations. |
| Fitted Distributions | Fail for pure specular cases (e.g., near point lights). |
| Specular Manifold Sampling (SMS) | Performance degrades for long chains; ignores energy distributions. |
Our Solution: Manifold Path Guiding
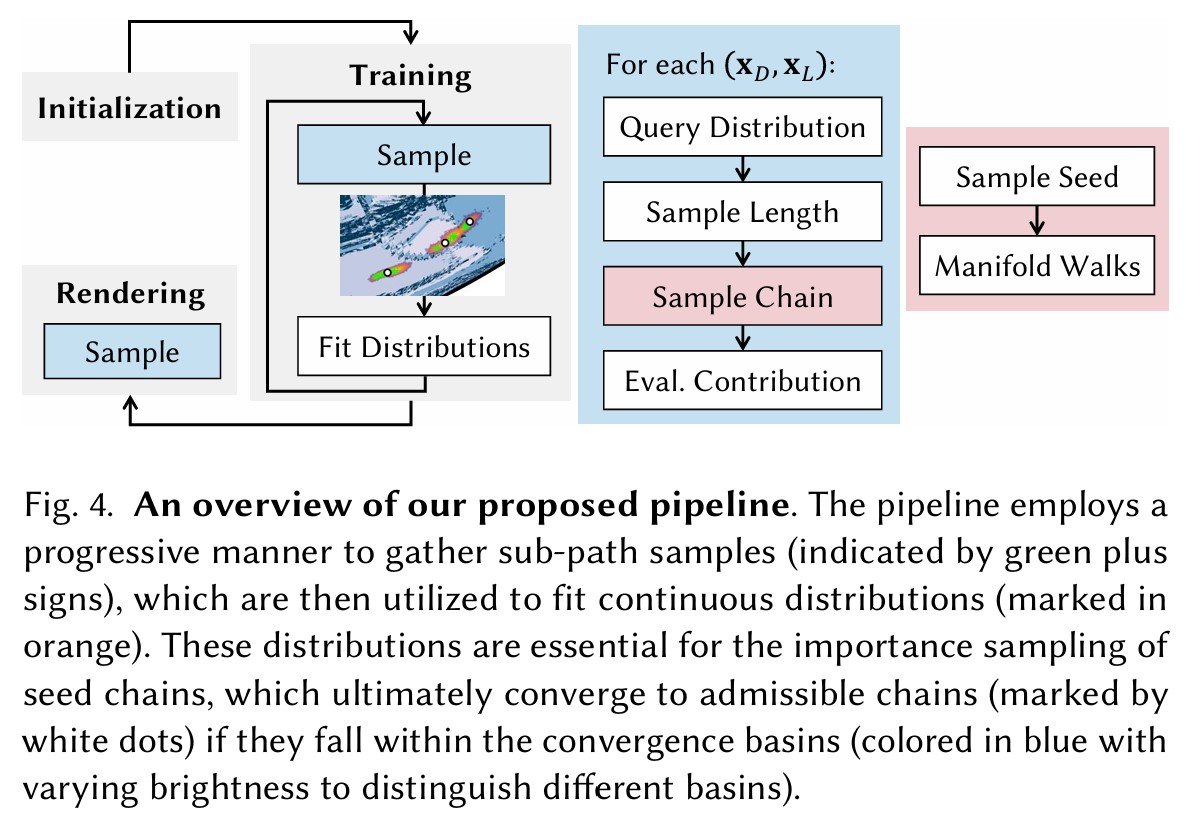
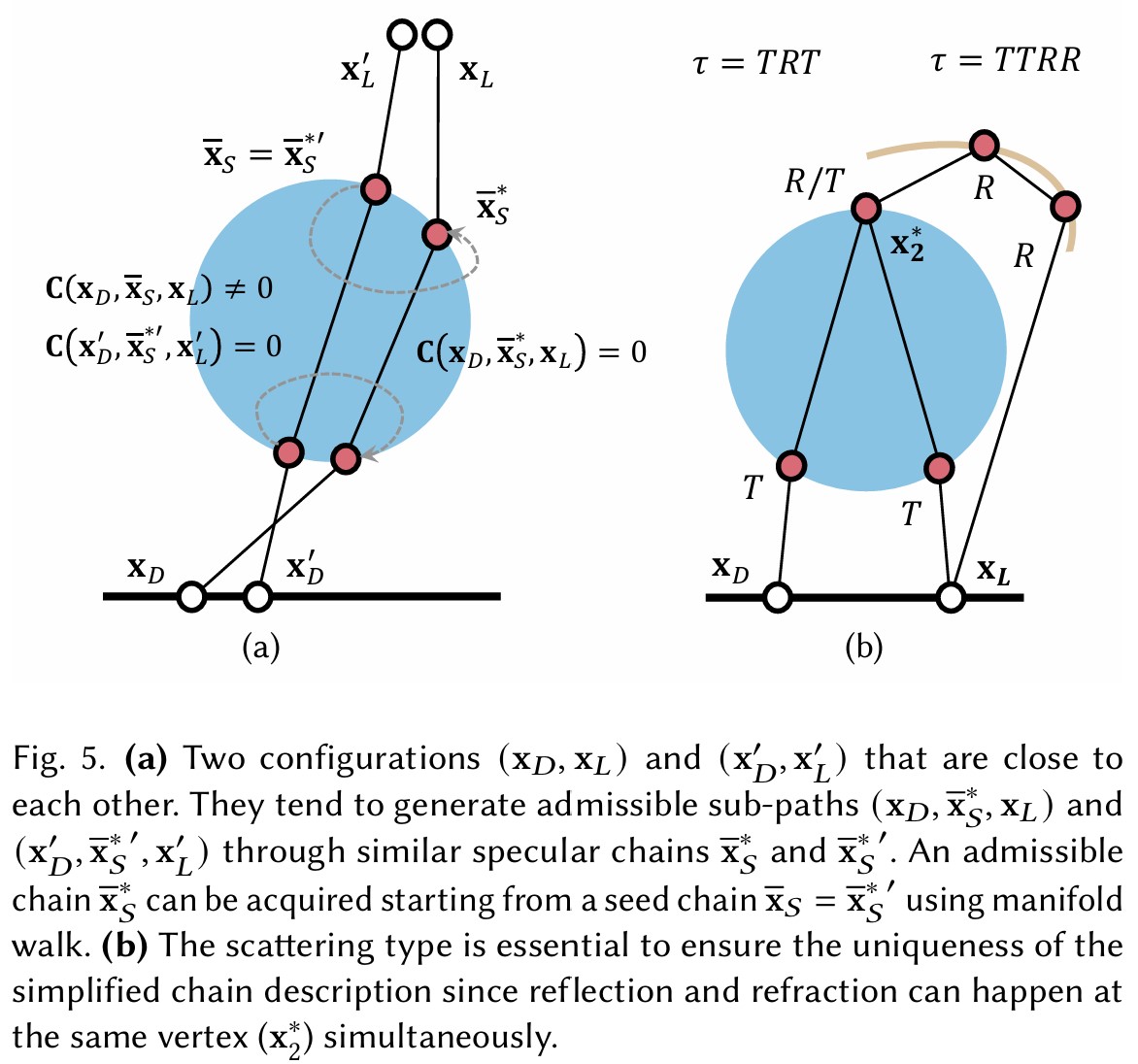
- Importance sample seed chains in a continuous space, then refine via manifold walks to converge to admissible chains.
- Exploit coherence in specular manifolds along with dimensionality reduction.
- Use converged distributions for efficient rendering.
Key Figures
Citation
@article{Fan23MPG,
title = {Manifold Path Guiding for Importance Sampling Specular Chains},
author = {Fan, Zhimin and Hong, Pengpei and Guo, Jie and Zou, Changqing and Guo, Yanwen and Yan, Ling-Qi},
journal = {ACM Trans. Graph.},
volume = {42},
number = {6},
year = {2023},
month = {Dec},
issue_date= {December 2023},
articleno = {257},
numpages = {14}
}
